Making Lightning Transactions Smart And Interactive With Structured Metadata 🚀

~ In the Summer of Bitcoin 2022, by Pavan Joshi
Bitcoin Transactions' New Future: A Wide Range of Usecases
Abstract
Bitcoin transactions hold only static data which doesn’t include much more relevant information to look into. What if transactions can have additional information (metadata)?
Better lightning network user experiences and improved Bitcoin apps are now possible thanks to specifications like WebLN.
Additionally, there are numerous broad uses such —
-
Bitcoin Sats-based instant payments made through a web browser (eg. Alby)
-
Gratuities for podcasters, streamers, and content creators
-
Streaming Sats
-
Online instant purchases and many more innovations were developed...
Transaction lists as we are familiar with them from our personal banking are frequently just a list of transactions arranged by date.
Every transaction contains information such as the Sender, Receiver, Amount, Reason, and Date. possess more data (metadata), like —
-
Transactional Goal
-
What was purchased in that specific transaction
-
Accessing items purchased directly from a wallet
-
Enable user interaction with transactions based on the extra data each transaction will have.
Every transaction has the potential to store more data in the form of metadata, which broadens the scope of interactive specifications like WebLN and expands the use cases for Bitcoin in many ways, paving the way for a new lightning network and Bitcoin in the future.
In order to make transactions containing static data more relevant and interactive, this research and technology specification intends to augment established technology standards like WebLN. It does this by enriching transactions with additional information as structured metadata.
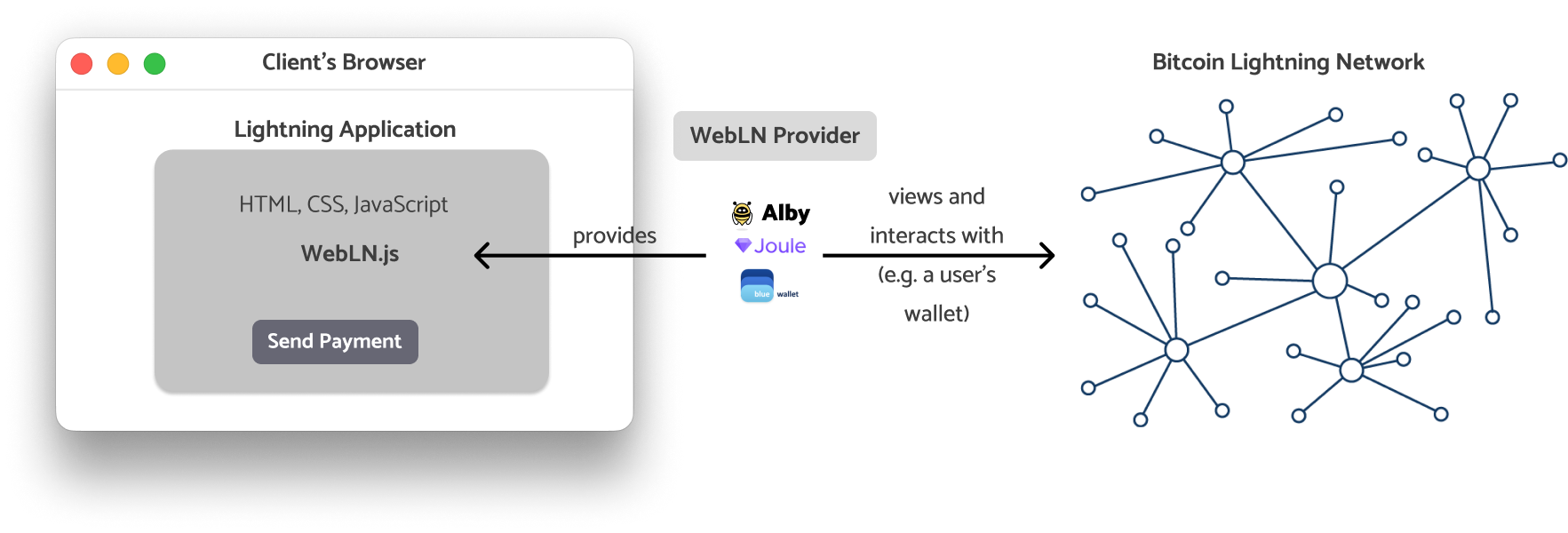
WebLN: What is it? 🤔
A web application powered by Bitcoin Lightning is created using the Lightning Web Standard (WebLN) specification.
To enable safe communication between web apps and users' lightning nodes, WebLN is a set of specifications for Lightning apps and client providers. It offers a programmatic, permissioned interface that enables apps to request payments from users, create invoices for payment receipts, and much more.
Know More About WebLN
To get knowledge of WebLN and its potential applications for your codebase, visit the official guide.
Extending WebLN
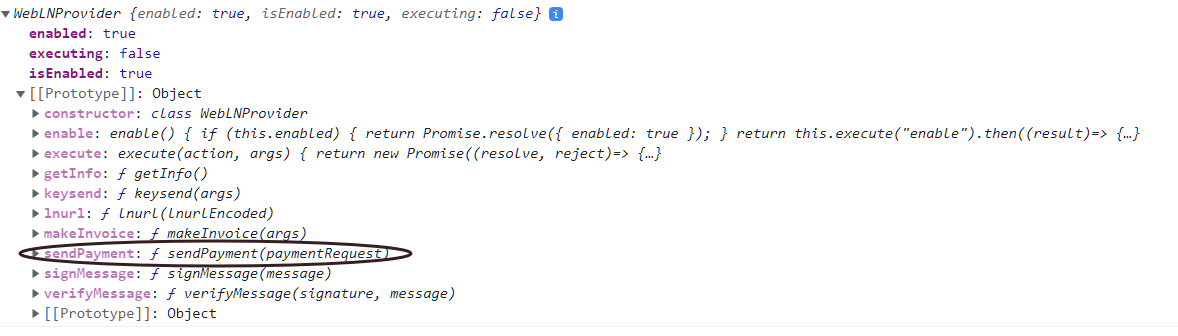
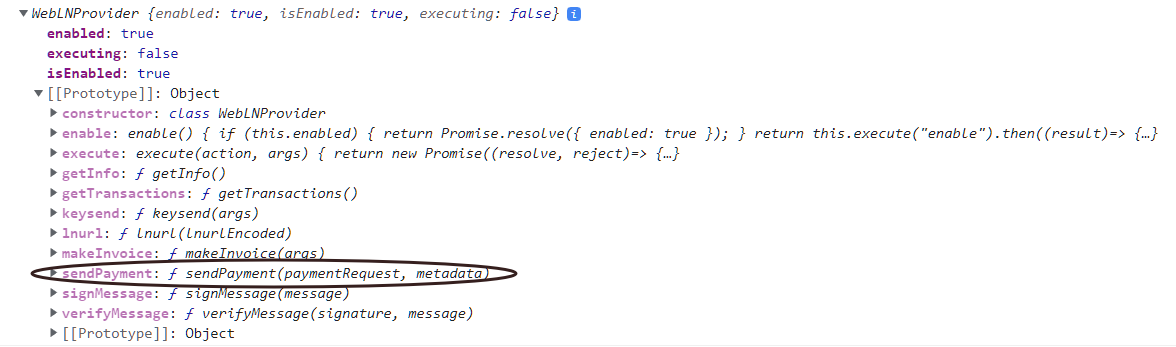
We may expand WebLN's sendPayment function to add an additional "optional" argument named metadata that will carry metadata as a string that can be provided to the Wallets. This function currently accepts a paymentRequest parameter holding a Bolt11 invoice.
Function Signature:
sendPayment(paymentRequest: string, metadata?: string): Promise<SendPaymentResponse>;
WebLN Provider presently linked by wallets
WebLN Provider attached by wallets after implementation of the spec
Working/architecture of this spec ⚙️
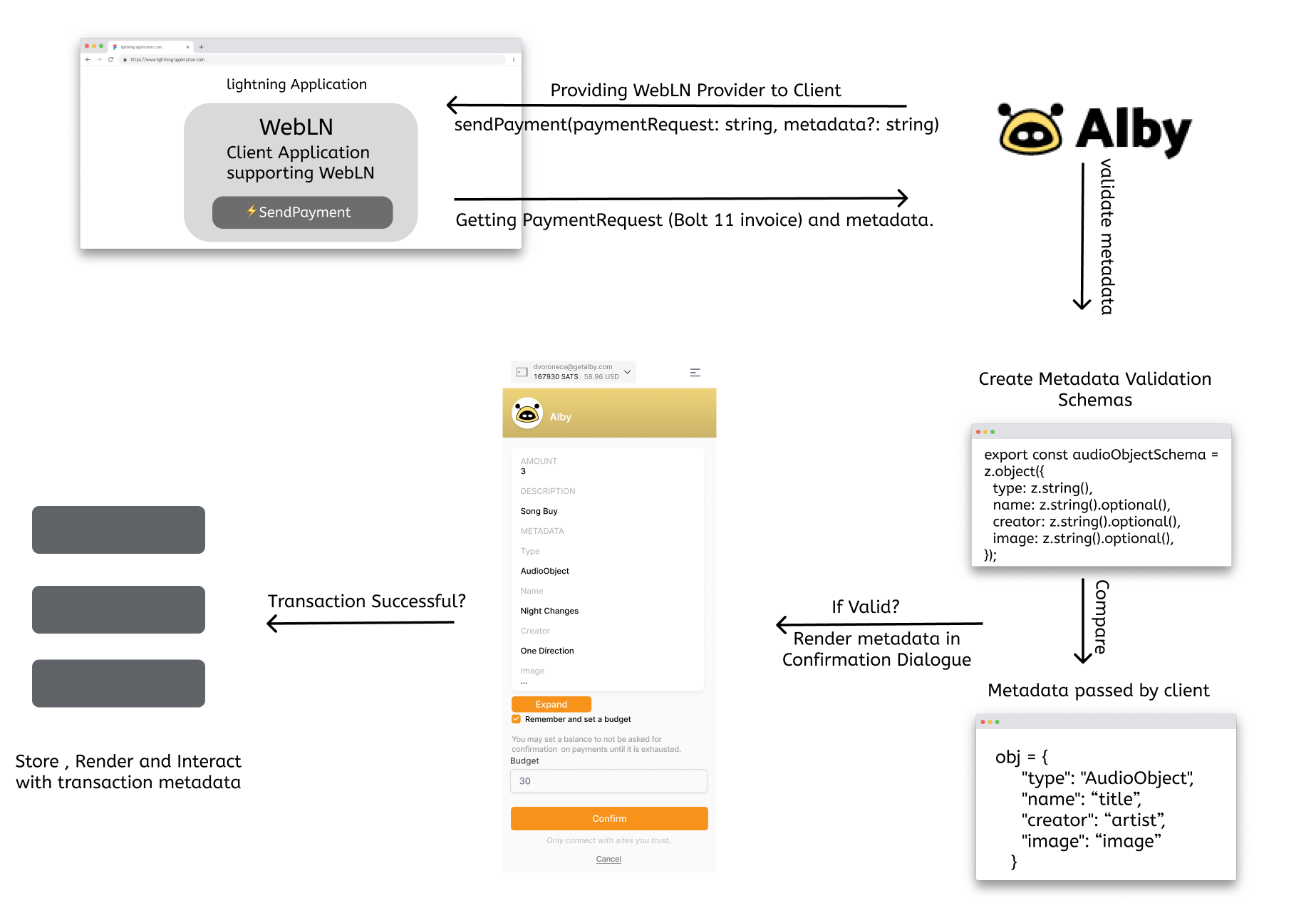
Overview
The specification runs through the fundamental five stages that clients and wallets must take to implement it.
-
Trigger SendPayment Method
-
Structure and Pass Metadata
-
Validate Metadata
-
Render Metadata in Confirmation Dialogue
-
Store, Interact and Perform After Actions
-
Trigger SendPayment Method
By activating the SendPayment method, a web application powered by Bitcoin Lightning and implementing the WebLN standard can ask for a WebLN provider.
sendPayment(paymentRequest: string, metadata?: string): Promise<SendPaymentResponse>; -
Structure and Pass Metadata
This specification defines several standard attributes that we use to express metadata and uses data models generated from standards like schema.org to give metadata structure.
Every data model has a type with a range of supported attributes that a lightning web application may use to organise metadata. Metadata is organised using data model classes like AudioObject, ImageObject, VideoObject, and many others.
Eg.
let metadata: {}; metadata = { "type": "AudioObject", "name": "title", "creator": "artist", "image": "image" }The lightning web application sends an invoice along with extra metadata using the SendPayment function. Such data is delivered to wallets by the WebLN provider.
webln.sendPayment(invoice, metadata); -
Validate Metadata
Metadata is created by users. Wallets must validate their accuracy. Wallets must validate metadata prior to taking any further action on it.
What is JSON Schema?🧐
A JSON media type for specifying the structure of JSON data is called JSON Schema.
A contract for what JSON data is needed and how to work with it is provided by JSON Schema.
To check received data against a preset data model, JSON schemas can be built and used.
There are numerous NPM validator packages that validate metadata and offer the following features:
-
Create a schema
-
Create a schema
-
Verify received data against that specific schema.
One of the validators used to verify JSON and object schema is the zod NPM package. The fact that this package has no external dependencies is its strongest feature.
The Zod NPM package has a validator method to check metadata against the preset schema
-
Schema Created using Zod NPM package
import { z } from "zod"; export const audioObjectSchema = z.object({ type: z.string(), name: z.string().optional(), creator: z.string().optional(), image: z.string().optional(), }); -
Metadata validation using a customised and reusable validator function
import { audioObjectSchema } from "./audioObjectSchema"; export function isBase64(str: string) { if (str === "" || str.trim() === "") { return false; } try { return btoa(atob(str)) == str; } catch (err) { return false; } } export function MetadataValidator(metadata: object) { let hasValidType: boolean = false; let hasValidImage: boolean = true; for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(metadata)) { if (key == "type") { if (value == "AudioObject") { const parsed = audioObjectSchema.safeParse(metadata); if (parsed.success) { hasValidType = true; } } } if (key == "image") { hasValidImage = isBase64(value); } } return hasValidType && hasValidImage; } -
To Validate metadata, call the function by passing metadata
const isMetadataValid = MetadataValidator(metadata);
-
-
Render Metadata in Confirmation Dialogue
If metadata is correctly validated, we may display to the user both the content of the metadata and the price they will be paying.
Here, consumers can review the information to understand the transaction's purpose before paying an invoice and have a clear understanding of everything before doing so.
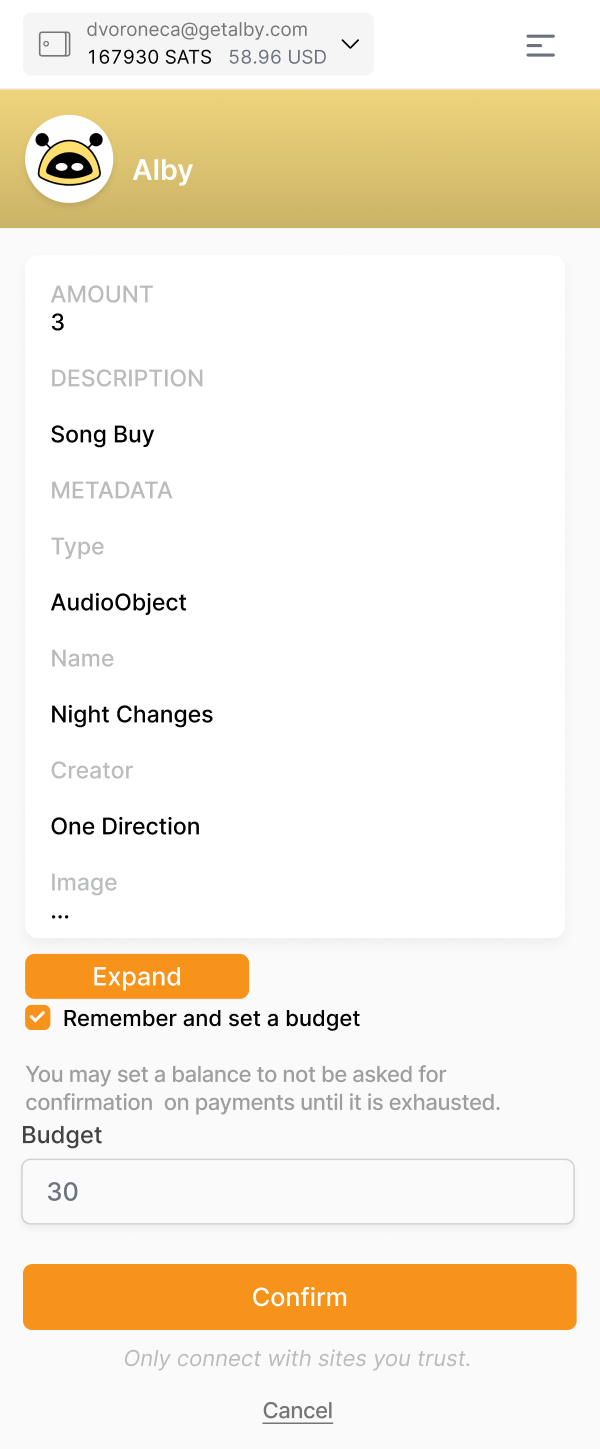
-
Store, Interact and Do After Actions
We can enable the user to access the purchased material once the payment is successful; additionally, the client application can enable the user to download a song following the successful payment.
Callback function for WebLN after actions
webln.sendPayment(invoice, metadata) .then(function (r) { // Required constraint to protect metadata as a rule while paying empty invoices if (r != undefined) { // Provide metadata after successful payment // Eg. Allow users to download a song after payment is successful } }) .catch(function (e) { alert("Failed: " + e.message); console.log('err pay:', e); });After actions on the wallet side
Transaction information can be utilised to describe both free and paid transactions (providing bought content in form of metadata).
Wallets can hold the contentUrl field as an optional field in a distinct column in their database, with the content of that field only being presented once payment has been received.
Use cases🔥
Payment transactions are now more interactive and engaging thanks to this new specification, which was created using Bitcoin and the Lightning Network and has a wide range of potential applications.
With the implementation of this specification, transactions will hold structured metadata of the consumed objects in addition to information about the payment that was made, opening up a wide range of use cases.
Users can, for instance, carry out the following tasks straight from their wallet:
-
accessing the digital content you've purchased.
-
renewing subscriptions that are about to expire.
-
promoting products by transmitting data as metadata.
-
Request donations with metadata containing the necessary details.
-
Open trades on trading platforms should be recalled.
-
boosting budgets for gift cards.
-
There is a tonne more use cases coming.
Resources📚
B Tech CE || GSoC2021 @CircuitVerse || GSOC'2022 Mentor @CircuitVerse || SOB'2022 @getAlby || Core Team Member @CircuitVerse || Open Source Enthusiast || Building spec to make lightning transactions smart